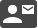
For the remaining weeks of winter, Orion, the celestial hunter is still residing high in the night sky. The prominent line of his three bright belt stars has sparked
legends and sky lore in many cultures past and present around the globe. This grouping goes by many names, such as Las Tres Marias, the Three Kings, Orion's
Belt, and in China, the three belt stars represent the Star Lords of Good Fortune Fu, Lu and Shu.
From the astrophysicist's point of view, this region represents one of the major parts of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which is about 1500 light-years distant
from our solar system. As the picture shows, the area is abundant with hot young stars, red emission nebulae, and bright and dark dust clouds. The striking red
band below the leftmost belt star, Alnitak, is IC 434, a hydrogen emission nebula that provides the backdrop for the famous Horsehead Nebula, Barnard 33. Right
on top of it is NGC 2024, a.k.a. the Flame Nebula, another emission nebula driven by energetic ultraviolet light coming from Alnitak. On the left side of the image, a
segment of the huge semicircular bow of Barnard's Loop glows with deep red. It is believed to be the remnant of a supernova that exploded about two million years
ago. At the center of the image there is a deep-sky object that is even spectacular when observed with the unaided eye, the large stellar grouping Cr 70. Collinder
70 is an OB association of more than 100 hot young stars centered around Alnilam, the middle of the belt stars. Cr 70 spans 2.5 degrees across and is easily visible
to the unaided eye when viewed from a dark location. With the aid of any binoculars it is simply stunning.
The image was shot by the astrophotography group project nightflight on 3 March 2014 on a moonless night on La Palma island from a spot 800 meters above sea
level. Total exposure time was 2 hours.
[Released February 9, 2015]
This project nightflight image was sponsored by